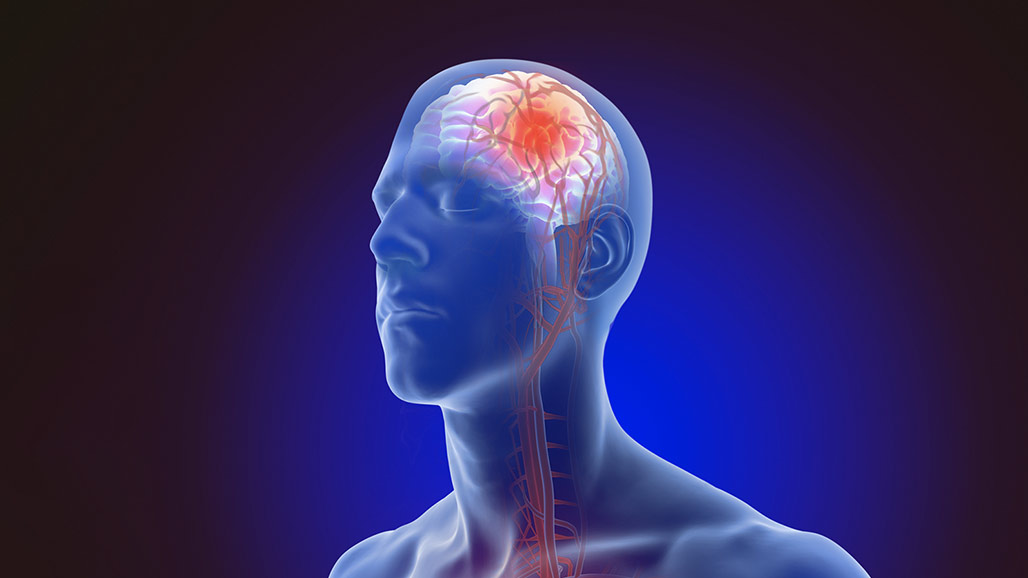
A stroke occurs when there is a rupture in the blood vessels of the brain. This causes bleeding and a shortage in blood flow to the brain. The overall effect can cause a shortage of blood and oxygen reaching the brain tissues. The brain cells and tissues need a constant supply of oxygen else they become damaged.

Some of the common symptoms:
- Trouble speaking or understanding what others are saying.
- Numbness or weakness on the face, arms and legs especially on one side of the body
- Confusion, Disorientation or lack of responsiveness
- Vision problems and dizziness
- Severe and sudden headache.
There are three main types of stroke:
Ischemic stroke: This is the most common type of stroke, making up 87% of all cases. A blood clot prevents blood and oxygen from reaching an area of the brain.
Hemorrhagic stroke: This occurs when a blood vessel ruptures. These are usually the result of aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)Trusted Source.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA): This occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is inadequate for a brief period of time. Normal blood flow resumes after a short amount of time, and the symptoms resolve without treatment. Some people call this a ministroke.
Stroke can be fatal. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), the age-adjusted mortality rate for 2017 was 37.6 in every 100,000Trusted Source stroke diagnoses. Doctors have made a great deal of progress in managing strokes, meaning that this mortality rate is 13.6% lower than it was in 2007.
Causes of stroke vary and are dependent on the type of stroke:
Ischemic Stroke can be caused by fatty deposits, blood clot or other debris blocking the blood vessels of the brain and this type of stroke is very common.
Hemorrhagic Stroke can be caused by uncontrolled high blood pressure, Trauma, Aneurysms, Cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
While Transient ischemic attack can be caused the same way as an Ischemic stroke but just temporary and with no severe damage. It normally subsides after some minutes.
Risk Factors:
Lifestyle – Overweight/Obese, Lack of exercise, heavy drinking and use of illegal drugs.
Medical – High BP, High Cholesterol, Diabetes, Cardiovascular diseases, Obstructive sleep apnea, personal or family history of stroke
Diagnosis:
Physical Examination, Blood test, CT and MRI scans, EKG, Cerebral Angiogram, Echocardiogram

Clot-breaking drugs, Mechanical Thrombectomy, Stents, Surgery, Clamping, Coiling etc. These treatment procedures vary with the type of stroke.
If you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of a stroke, it’s vital that you seek emergency medical treatment as soon as possible.